Guarantees of Origin (GOs) are an instrument of proof of source of electricity being sold in retail market. Just GOs enable final consumers both to choose any type of electricity generation and confidence that electricity they receive is from renewable sources. Companies buy GOs as the latter ones are an effective instrument for decarbonization of the economy, the basis for calculating carbon footprints and reporting on sustainability. The Greenhouse Gas Protocol, the most widely used emissions reporting tool in international accounting, allows GOs to be used for carbon reporting; this is the primary source of business demand for GOs. USAID ESP Electricity Market Expert Danylo Babkov explains how an instrument of GOs works, how companies can use them, and what has to be done for GOs mechanism implementation in Ukraine.
Not only do GOs provide customers with information on the origin of their electricity, but they are also an instrument of support to renewable energy (RE) producers. In European trading platforms the RE producers sell the GOs to electricity traders or retail suppliers who, in their turn, offer them to interested commercial consumers. In Ukraine, considering the current RE support mechanism, the GOs framework must be designed in such a way that it would be possible to redirect the revenue from GOs to Ukrenergo or Guaranteed Buyer – guarantors of green subsidies, as an additional monetary support for compensation of losses from feed-in-tariff mechanism. Such mechanism principle should be in place during the whole support period under feed-in-tariff till 2029.
The GOs mechanism in Energy Community (EnC) member countries is becoming more relevant because the European Union (EU) will soon adopt legislation on the Green Deal and the Carbon Borders Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM). Currently, almost all Emissions Trading System allowances in the European electricity sector are auctioned. Electricity generators from non-EU countries can export electricity without it being subject to carbon taxes (unless their own country applies such taxes). As a result, non-EU exporters have an advantage over EU suppliers. When CBAM enters into force in 2023, all electricity exports will be subject to carbon taxes, except for electricity produced from RE sources. To take advantage of this exception, RE producers/exporters will have to prove that their energy is generated using renewable sources, which can be done with GOs.
As of January 2022, Ukraine has 10 gigawatts of installed RE generating capacity, it is about 15 TW.h of electricity per year that is a significant potential to increase electricity exports, it will become possible after Ukraine’s energy system synchronizes with the European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity (ENTSO-E). The potential income from sale of Guarantees of origin can balance financial indicators of the Guaranteed Buyer as main guarantor of feed-in-tariff, namely: improve liquidity and payment discipline. Given the importance of electricity exports for the economy of Ukraine, having a functioning GOs mechanism will be crucial once CBAM is the law.
How the guarantees of origin market are organized
Directive 2009/28/EC requires European Community members to accept GOs issued by other EU members. To harmonize the use of GOs and support trade, the Association of Issuing Bodies (AIB) launched the European Energy Certificate System (EECS) in 2007 to develop standards for GOs. The unified certification system is designed to standardize issuance, trade, and cancellation of GOs that, in its turn, facilitates the unified rules of cross-border trade in European electronic hub platform. Its standards are governed by principles and rules of operations accepted by all participants, each country implemented them using its own domain protocol. Any government that wants to participate in the EECS system and its electronic hub must first set up a domain protocol with incorporated EECS rules, and the AIB must approve this protocol before the country can start issuing GOs.
One of the main conditions for GOs to succeed is high demand, both nationally and across Europe. Ukrainian regulators should promote that commercial consumer are aware of GOs.
As the development of the European GO market shows, demand for GOs has been relatively stable in recent years.
How guarantees of origin are issued
The common practice of the EU countries is the market participants should firstly open an account with the central electronic GOs registry that is become possible after transmission system operator certified the RES-based electricity generation devices. After registration of electronic account, the participant may apply the registry operator for issuance of GO (guarantees are issued based on commercial metering data on calculations of transmission system operator. The guarantee owning and trading is generally not restricted, but usually only companies registered in the wholesale electricity market (generators, traders, suppliers) apply for opening an account.
Auctions for guarantees of origin
To hold a GO auction, the registry operator (suppose, in Ukraine it will be TSO) issues GOs, based on RES-based electricity generation volume of separate plant, following the commercial metering, issues the GOs, which meet the generation volume. For instance, 206 mln. kW.h of electricity meet 206.000.000,00 lots of Guarantees of Origin. Then the registry operator displays the volume of GOs in its own electronic account and publicly announces auctioning on the selected trading platform.
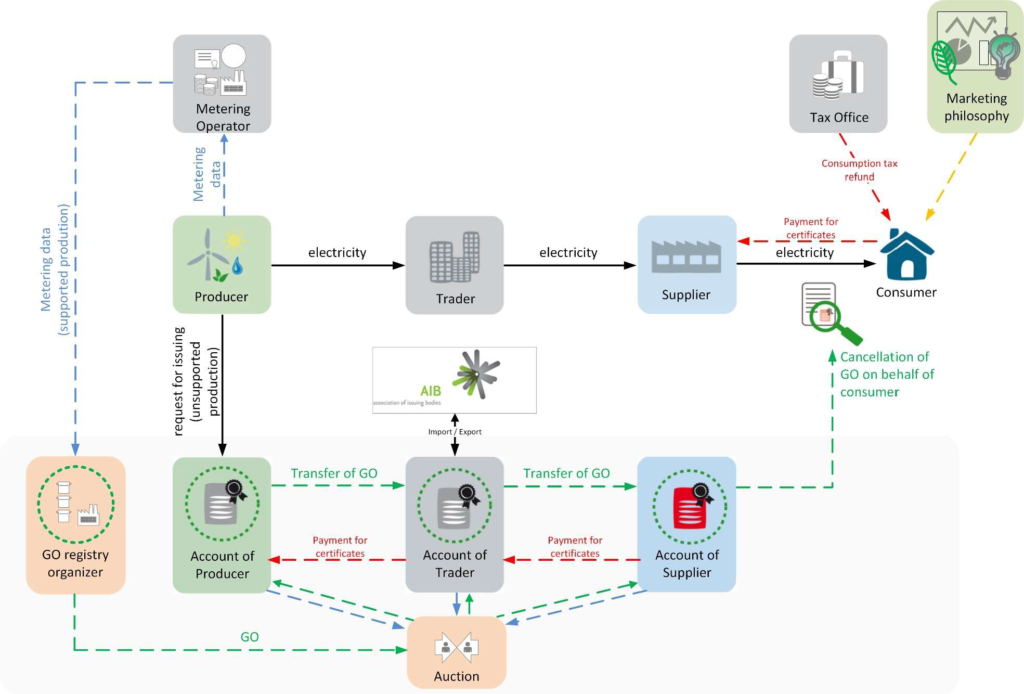
In this situation, the registry operator, namely, TSO is a legal successor and seller of GOs. Bidders offer the highest price they are willing to pay for GOs, the winner will be decided following this principle. As soon as the GO reaches the final consumer then such GO is cancelled. As it was mentioned earlier, the funds from GO sale can be used as an additional cash flow to ensure RES financial support – as a result of GOs sale the TSO can receive new stream of profit, which can be provided to Guaranteed Buyer under feed-in-tariff RES support model. The TSO transmission tariff will respectively decrease proportionally with new profit from GOs that will, finally, be benefitted by end electricity consumers. Any GOs transactions are executed via electronic registries in any Internet browser easy to user.
Implementation in Ukraine
In 2012, Ukraine committed to implement the GO mechanism through an EnC Ministerial Council decision. Under Article 15 of the first Renewable Energy Directive, EnC Contracting Parties (CPs) including Ukraine agreed to develop national GO legislation and designate national authorities responsible for implementing the mechanism. A year later, Ukraine adopted the Decree On Approval of the Procedure for Issuance, Use, and Termination of Guarantees of Origin for Electricity for Economic Entities that Produce Electricity from Alternative Energy Sources. However, the State Agency on Energy Efficiency and Energy Saving (the designated authority) has not yet implemented an electronic system compatible with the EECS. In November 2020, the EnC encouraged Ukraine to establish the GO system without further delay.
In March 2021, the EnC Secretariat issued a Discussion Paper on implementing GOs in the EnC, proposing a Community-wide approach. Under this plan, the EnC would help set up a regional GO mechanism, covering the national markets of all or selected CPs, and consider implementing it through a centralized IT platform by June 2022. At the same time, the EnC would facilitate “observer status” for CPs in the AIB and enable AIB countries to export their GOs to the CPs’ national markets.
In line with the current Renewable Energy Directive (2009/28/EC), all CPs have a legal basis to manage their own GOs and most have designated the authorities who will manage the mechanism and establish electronic systems (platforms) for issuing and trading GOs.
In Ukraine, laws need to be updated. Furthermore, choosing the GO issuing authority remains an open question: will it be the State Agency on Energy Efficiency and Energy Saving or the transmission system operator (TSO), Ukrenergo? In EnC countries, the TSO often holds this function. The main reason is that TSOs administer commercial metering, which means they have the data and resources to verify and confirm the origin of the electricity supplied by RE producers. TSOs also have expertise in implementing other systems and software products to operate the grid and run balancing and ancillary services markets, which require the physical and financial settlement of electricity generation.
The way forward for Ukraine’s guarantees of origin
The EnC Secretariat is now developing a Unified Regional Electronic Register for Guarantees of Origin, which will be ready by the third quarter of 2022. As a member of the EnC, Ukraine has an opportunity to launch its GO mechanism and join the Regional GO Trade System fairly quickly. However, the country must first harmonize its legislation with the relevant Energy Community directives. With the support of the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID), the Energy Security Project (ESP) is helping Ukraine work through the legal, technical, and outreach steps it must take to bring this plan to fruition.
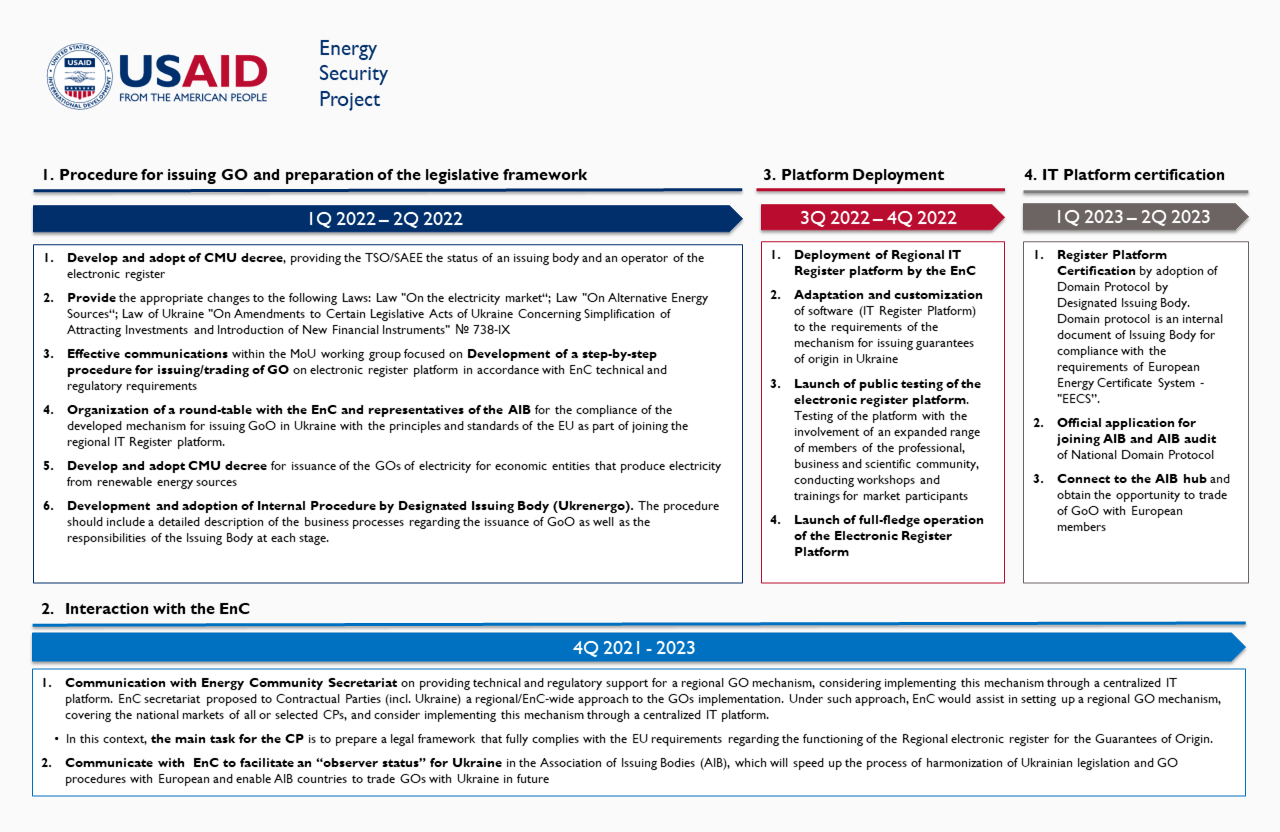
Ukraine has all chances to join the system and incentivize RE production, brings transparency of the origin of electricity for its consumers, and further integrates Guarantees of Origin, as a new energy product, with European energy market. Onwards and upwards!
